A main cause of depersonalization derealization disorder are high anxiety levels. The sample size, in Lara Nataccis 2018 study on the effect of Omega 3 and anxiety disorders [1], consisted of 12.268 adults. The study showed that with higher n-3 intake as well as lower n-6/n-3 ratios, the likelihood of an adult having an anxiety disorder decreased.
Why Is Omega 3 Relevant for DPDR?
- Omega 3 fatty acids play an important role in your brain.
- For instance, brain cell signalling mechanisms, which include serotonergic and dopaminergic pathways are modulated by omega-3 fatty acids [2].
- On a side note I had my serotonin levels checked during my DPDR and they were low.
- Omega-3 contribute to neurobiological activities such as neuroplasticity, anti-oxidation and anti-inflammatory, which may be linked to psychotropic effects [3]
- Omega 3 influences mental health as a handful of studies suggest [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Research that suggest a link between Omega 3 and mental health
| Source | Key Result | How is this relevant for DPDR? |
| [1] | A study analysing 12.268 participants found that omega-3 and the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio impacts the likelihood of an adult having an anxiety disorder. | Tons of DPDR sufferers, including myself, link depersonalization to anxiety, thus research concerning anxiety disorders is a promising place to look for answers as long as research on DPDR is still insufficient. |
| [4] | Omega 3 is an effective supplement that can help mitigate symptoms of psychiatric disorders symptoms. | DPDR is a psychiatric disorder. |
| [5] | 68 participants took part in a trial in which half were given omega 3 and the other half took placebos over a period of 3 months. 20% of the participants which received omega 3 supplementation showed a 20% reduction in anxiety symptoms | DPDR is linked to anxiety on a consistent basis. |
| [6] | A 3-month trial with 22 participants resulted in a significant decrease in the participants anxiety levels | Again, DPDR is linked to anxiety on a consistent basis. |
| [2] | Effective in mood disorders, unipolar and bipolar depression and some evidence for effectiveness in borderline personality disorder | Being effective in the treatment of other disorders might suggest it could also help with DPDR |
What are Omega 3 and 6 fatty acids?
Fatty acids are a part of the fat molecule, and fat is part of our diet. Omega-3 fatty acids (omega 3, ω-3, n-3) as well as omega-6 fatty acids (omega 6, ω-6, n-6) are specific types of fatty acids.
Where do Omega 3 and Omega 6 come from?
Omega 3: Common foods high in omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish, fish oils, eggs, flax seeds, chia seeds, flaxseed oil, and walnuts.
Omega 6: Common foods high in omega-6 include fast food, processed snacks, cakes, everything deep fried, sunflower oils, corn, soybeans, walnuts, safflower oil and peanut butter
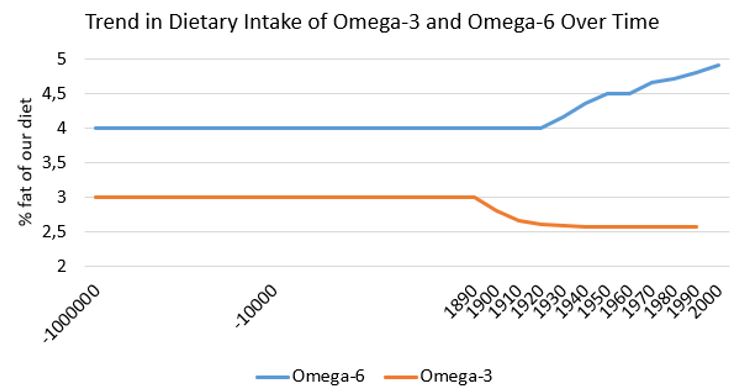
Change of Intake of Omega 3 and 6 Over Time.
We are what we eat
Hippocrates
The diagram [7] below depicts how our omega-6 and omega-3 intake has changed over time. Please note, our DNA composition hasn’t changed over the past 100000 years, but our diet has. Put into perspective the findings of Lara Nataccis 2018 study [1] in which anxiety disorders decrease with higher Omega-3 intake and lower omega-6 to omega-3 ratios, this dietary trend should be taken into consideration while searching for DPDR remedies.
My DPDR experience and Omega 3 intake.
- I took omega 3 daily during my DPDR recovery, because of the overwhelmingly large amount of scientific data proving it’s benefits for brain function and overall health.
- Nevertheless, I could not feel any change in my DPDR directly after taking a fish oil capsule, as e.g. I did with Enterosgel or Caster Oil.
- I can still highly recommend taking it daily, since I did recover from DPDR rapidly and it might have played a role.
Conclusion – Omega 3 and Depersonalization
Healthline published an article [8] stating the following:
“People who ate a pre-industrial diet had an omega-6 to omega-3 ratio of about 4:1 to 1:4, most falling somewhere in between. The ratio today is 16:1, much higher than what people are genetically adapted to”.
Healthline [8]
Thus, increase your omega 3 intake, e.g. via supplements and decrease your omega 6 intake, thus eat less deep-fried crap! You need your body to function as good as possible which will help decrease your cortisol levels (stress) which in my experience will get you the chance to speed up your DPDR recovery. Hang in there!
Related Questions
Does acceptance and patients cure depersonalization and derealization? One of the major keys to my DPDR recovery was acceptance and patients. Acceptance and patients lets you focus on living a meaningful life, which can speed up your DDD recovery. It has been mentioned by tons of DDD recoveries and scientific work. If you want to learn more about the positive effects of acceptance and patience you can have a look here: “How To Cure Depersonalization Naturally? Acceptance And Patience!“
What’s the difference between depersonalization and derealization?
Scientific definition:
- Depersonalization is a mental disorder in which the patient feels unreal, fake, numb, as though they lack emotion and or is disconnected from their body. Nevertheless, the patient still passes the reality check, meaning they notice that something is wrong.
- Derealization is a mental disorder in which the patient perceives his or her surroundings as unreal, fake, two dimensional or as in a dream. Nevertheless, the patient still passes the reality check, meaning they notice that something is wrong.
For more information on what DPDR actually is, I have written the following post for you: “How To Cure Depersonalization Naturally? What Is DPDR“
References
[1] Natacci L, M Marchioni D, C Goulart A, et al. Omega 3 Consumption and Anxiety Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Nutrients. 2018;10(6):663. Published 2018 May 24. doi:10.3390/nu10060663
[2] Bozzatello P, Brignolo E, De Grandi E, Bellino S. Supplementation with Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review of Literature Data. J Clin Med. 2016;5(8):67. Published 2016 Jul 27. doi:10.3390/jcm5080067
[3] Su KP, Matsuoka Y, Pae CU. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Prevention of Mood and Anxiety Disorders. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2015;13(2):129-137. doi:10.9758/cpn.2015.13.2.129
[4] Guesnet P, Alessandri JM. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and the developing central nervous system (CNS) – Implications for dietary recommendations. Biochimie. 2011;93(1):7-12. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2010.05.005
[5] Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Belury MA, Andridge R, Malarkey WB, Glaser R. Omega-3 supplementation lowers inflammation and anxiety in medical students: a randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Nov;25(8):1725-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.07.229.
[6] Buydens-Branchey L, Branchey M, Hibbeln JR. Associations between increases in plasma n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids following supplementation and decreases in anger and anxiety in substance abusers. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32(2):568-575. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.10.020
[7] https://spitzen-praevention.com/wissen/ernaehrung/omega-3-und-omega-6-fettsaeuren-die-grundlagen/
[8] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/optimize-omega-6-omega-3-ratio#TOC_TITLE_HDR_3